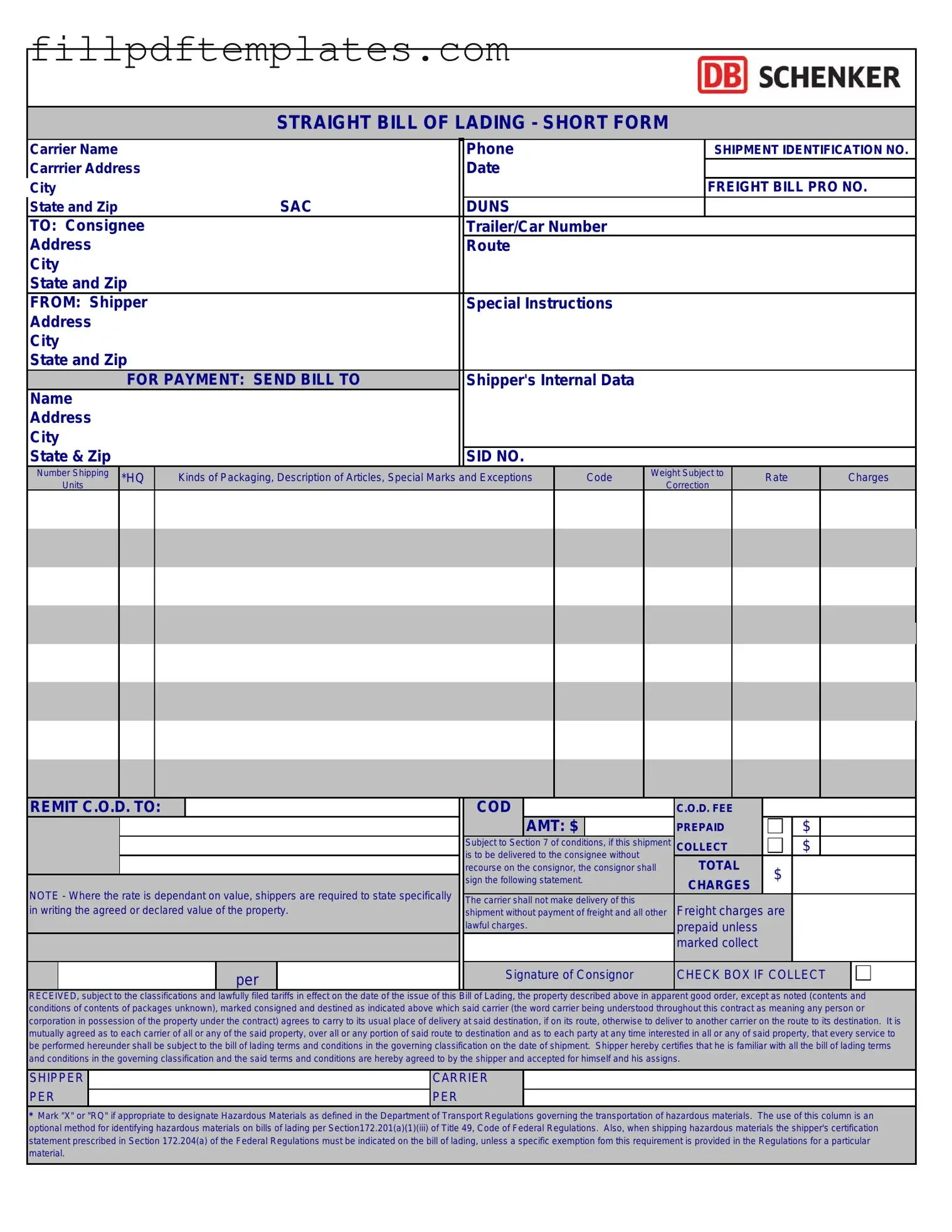
Fill a Valid Straight Bill Of Lading Template
The Straight Bill of Lading is a crucial document in the shipping and logistics industry, serving as a receipt for goods and a contract between the shipper and carrier. This form is particularly important for transactions where the goods are shipped directly to a specific recipient, as it ensures that only the designated party can claim the shipment. Unlike other types of bills of lading, the Straight Bill of Lading is non-negotiable, meaning it cannot be transferred to another party. This characteristic provides a layer of security for both the shipper and the recipient, as it clearly defines ownership and responsibilities. The form typically includes essential details such as the names and addresses of the shipper and consignee, a description of the goods, and terms of transportation. Additionally, it may outline any special instructions or requirements for handling the shipment. Understanding the various components and implications of the Straight Bill of Lading is vital for anyone involved in the transportation of goods, as it helps facilitate smooth transactions and reduces the risk of disputes.
Additional PDF Templates
Fedex Freight Truck - Shippers must fill out the necessary information for effective delivery.
The Pennsylvania Motor Vehicle Bill of Sale form is a crucial document in the transfer of ownership for motor vehicles. It provides a record that includes vital information such as the buyer's and seller's details, vehicle specifications, and the sale price. For those looking to ensure a smooth transaction, the Bill of Sale for a Motor Vehicle is an essential resource that protects the interests of both parties involved.
Hub Certification Texas - It aids in understanding the flow of membership units within the company.
Similar forms
The Straight Bill of Lading is an important document in the shipping and transportation industry. It serves as a receipt for goods and outlines the terms under which those goods are being transported. There are several other documents that share similarities with the Straight Bill of Lading. Here are ten of them:
- Bill of Lading (BOL): Like the Straight Bill of Lading, a standard Bill of Lading serves as a contract between the shipper and carrier. It outlines the details of the shipment and can be negotiable or non-negotiable.
- Air Waybill: This document is used for air transport. Similar to a Straight Bill of Lading, it acts as a receipt for the goods and outlines the terms of the shipment, but it is not a document of title.
- Warehouse Receipt: A Warehouse Receipt is issued by a storage facility. It confirms the receipt of goods and outlines the terms of storage, similar to how a Straight Bill of Lading confirms the receipt of goods for transport.
- Freight Bill: This document details the charges for transportation services. While a Straight Bill of Lading serves as a contract for the shipment, the Freight Bill focuses on the financial aspects of the transport.
- Operating Agreement: This document is essential for Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) as it outlines the management structure and operating procedures. By utilizing the Operating Agreement form, LLC members can clearly define their rights and responsibilities, thereby preventing disputes and ensuring smooth operations within the company.
- Delivery Order: A Delivery Order instructs the carrier to release goods to a specified party. This document is similar to a Straight Bill of Lading in that it facilitates the transfer of goods, but it is used after the goods have arrived.
- Import/Export Declaration: This document is required by customs authorities. It provides details about the goods being imported or exported, similar to how a Straight Bill of Lading provides information about the shipment.
- Customs Invoice: A Customs Invoice is used for international shipping to declare the value of goods. Like the Straight Bill of Lading, it provides essential information about the shipment for regulatory purposes.
- Certificate of Origin: This document certifies the country of origin of the goods. While it serves a different purpose, it is similar in that it provides necessary information about the shipment.
- Packing List: A Packing List details the contents of a shipment. It complements the Straight Bill of Lading by providing additional information about the items being transported.
- Consignment Note: This document is used in road transport. It serves a similar purpose to a Straight Bill of Lading by confirming the details of the shipment and the agreement between the shipper and carrier.
Document Specifics
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Definition | A Straight Bill of Lading is a document that serves as a receipt for goods and a contract for their transportation. It is specifically made out to a named consignee. |
| Transferability | This type of bill of lading is non-negotiable. It means that the goods can only be delivered to the named consignee and cannot be transferred to another party without consent. |
| Governing Law | In the United States, the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) governs bills of lading, including the Straight Bill of Lading, across various states. |
| Use Cases | Commonly used in domestic shipping, a Straight Bill of Lading is ideal for transactions where the buyer and seller have a trusted relationship, ensuring secure delivery. |
Things You Should Know About This Form
-
What is a Straight Bill of Lading?
A Straight Bill of Lading is a document issued by a carrier that serves as a receipt for goods being transported. It is a legally binding contract between the shipper and the carrier, detailing the terms of the shipment. Unlike an order bill of lading, a straight bill of lading is non-negotiable, meaning that it cannot be transferred to another party. This type of bill typically indicates that the goods are consigned directly to a specific recipient.
-
What information is included in a Straight Bill of Lading?
A Straight Bill of Lading contains several key pieces of information, including:
- The name and address of the shipper
- The name and address of the consignee (the recipient)
- A description of the goods being shipped, including weight and quantity
- The shipping route and any specific instructions
- The date of shipment
- Carrier information, including signature and date
This information ensures that all parties involved understand the terms of the shipment and can track the goods as they move through the supply chain.
-
What are the advantages of using a Straight Bill of Lading?
Using a Straight Bill of Lading offers several advantages:
- Simplicity: The non-negotiable nature makes it straightforward for the shipper and consignee, eliminating the need for additional endorsements.
- Security: Because it is issued directly to a specific recipient, it reduces the risk of theft or fraud.
- Clarity: It provides clear documentation of the terms of shipment, which can help resolve disputes if they arise.
These benefits make it a popular choice for many businesses when shipping goods.
-
How does a Straight Bill of Lading affect liability?
The Straight Bill of Lading plays a significant role in determining liability during transit. Once the carrier takes possession of the goods, they assume responsibility for their safe transport. If damage or loss occurs, the shipper or consignee can file a claim against the carrier based on the terms outlined in the bill of lading. It is essential to review these terms carefully, as they may limit the carrier's liability under certain conditions. Understanding these nuances can help you make informed decisions and protect your interests.
Documents used along the form
The Straight Bill of Lading is a crucial document in the shipping and freight industry, serving as a receipt for goods and a contract between the shipper and the carrier. However, several other forms and documents are often used alongside it to ensure a smooth transportation process. Below is a list of these essential documents, each playing a unique role in the logistics chain.
- Commercial Invoice: This document outlines the transaction between the buyer and seller, detailing the goods sold, their value, and payment terms. It serves as a basis for customs declarations.
- Packing List: This list provides detailed information about the contents of a shipment, including item descriptions, quantities, and weights. It helps both the shipper and receiver verify the shipment's contents.
- Certificate of Origin: This document certifies the country in which the goods were manufactured. It may be required for customs clearance and to determine tariffs.
- Operating Agreement: For those establishing a business structure, refer to our detailed Operating Agreement form requirements to ensure compliance and clarity in your operations.
- Insurance Certificate: This certificate provides proof of insurance coverage for the goods during transit. It protects against loss or damage and is essential for risk management.
- Import/Export License: Required for certain goods, this license authorizes the import or export of specific products, ensuring compliance with national regulations.
- Delivery Receipt: This document is signed by the recipient upon delivery, confirming that the goods have been received in good condition. It serves as proof of delivery.
- Freight Bill: This bill details the charges associated with transporting goods. It includes information on the shipment, such as weight, dimensions, and destination.
- Customs Declaration: This document is submitted to customs authorities, detailing the nature of the goods being imported or exported. It is vital for compliance with customs regulations.
- Export Packing List: Similar to the packing list, this document is tailored for international shipments and includes additional information required by customs in the destination country.
Understanding and utilizing these documents alongside the Straight Bill of Lading can streamline the shipping process and mitigate potential issues. Each document serves a specific purpose and contributes to the overall efficiency of logistics and transportation. It is essential to ensure that all necessary paperwork is completed accurately and submitted in a timely manner.
Straight Bill Of Lading Preview
STRAIGHT BILL OF LADING - SHORT FORM
Carrier Name |
|
|
Phone |
|
|
SHIPMENT IDENTIFICATION NO. |
||
Carrrier Address |
|
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
City |
SAC |
|
|
|
|
FREIGHT BILL PRO NO. |
||
State and Zip |
|
DUNS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
TO: Consignee |
|
|
Trailer/Car Number |
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
|
|
Route |
|
|
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State and Zip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FROM: Shipper |
|
|
Special Instructions |
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State and Zip |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FOR PAYMENT: SEND BILL TO |
|
Shipper's Internal Data |
|
|
|
|
||
Name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
State & Zip |
|
|
SID NO. |
|
|
|
|
|
Number Shipping *HQ |
Kinds of Packaging, Description of Articles, Special Marks and Exceptions |
Code |
Weight Subject to |
Rate |
Charges |
|||
Units |
|
|
|
|
Correction |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REMIT C.O.D. TO: |
|
|
|
|
COD |
|
|
C.O.D. FEE |
|
|
|
|
||
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AMT: $ |
|
PREPAID |
|
$ |
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
|
Subject to Section 7 of conditions, if this shipment |
COLLECT |
|
$ |
|
|
|||
State & Zip |
|
|
|
|
|
is to be delivered to the consignee without |
TOTAL |
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
recourse on the consignor, the consignor shall |
$ |
|
|
|
|||||
NOTE - Where the rate is dependant on value, shippers are required to state specifically |
|
sign the following statement. |
CHARGES |
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
|
The carrier shall not make delivery of this |
Freight charges are |
|
|
|
|||||||||
in writing the agreed or declared value of the property. |
|
shipment without payment of freight and all other |
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
lawful charges. |
prepaid unless |
|
|
|
|
||
The agreed or declared vlaue of the property is hereby specifically stated by the shipper to |
|
|
|
|
marked collect |
|
|
|
|
|||||
be not exceeding |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
$ |
|
|
|
per |
|
|
Signature of Consignor |
CHECK BOX IF COLLECT |
|
|||||
RECEIVED, subject to the classifications and lawfully filed tariffs in effect on the date of the issue of this Bill of Lading, the property described above in apparent good order, except as noted (contents and conditions of contents of packages unknown), marked consigned and destined as indicated above which said carrier (the word carrier being understood throughout this contract as meaning any person or corporation in possession of the property under the contract) agrees to carry to its usual place of delivery at said destination, if on its route, otherwise to deliver to another carrier on the route to its destination. It is mutually agreed as to each carrier of all or any of the said property, over all or any portion of said route to destination and as to each party at any time interested in all or any of said property, that every service to be performed hereunder shall be subject to the bill of lading terms and conditions in the governing classification on the date of shipment. Shipper hereby certifies that he is familiar with all the bill of lading terms and conditions in the governing classification and the said terms and conditions are hereby agreed to by the shipper and accepted for himself and his assigns.
SHIPPER |
|
CARRIER |
|
PER |
|
PER |
|
*Mark "X" or "RQ" if appropriate to designate Hazardous Materials as defined in the Department of Transport Regulations governing the transportation of hazardous materials. The use of this column is an optional method for identifying hazardous materials on bills of lading per Section172.201(a)(1)(iii) of Title 49, Code of Federal Regulations. Also, when shipping hazardous materials the shipper's certification statement prescribed in Section 172.204(a) of the Federal Regulations must be indicated on the bill of lading, unless a specific exemption fom this requirement is provided in the Regulations for a particular material.